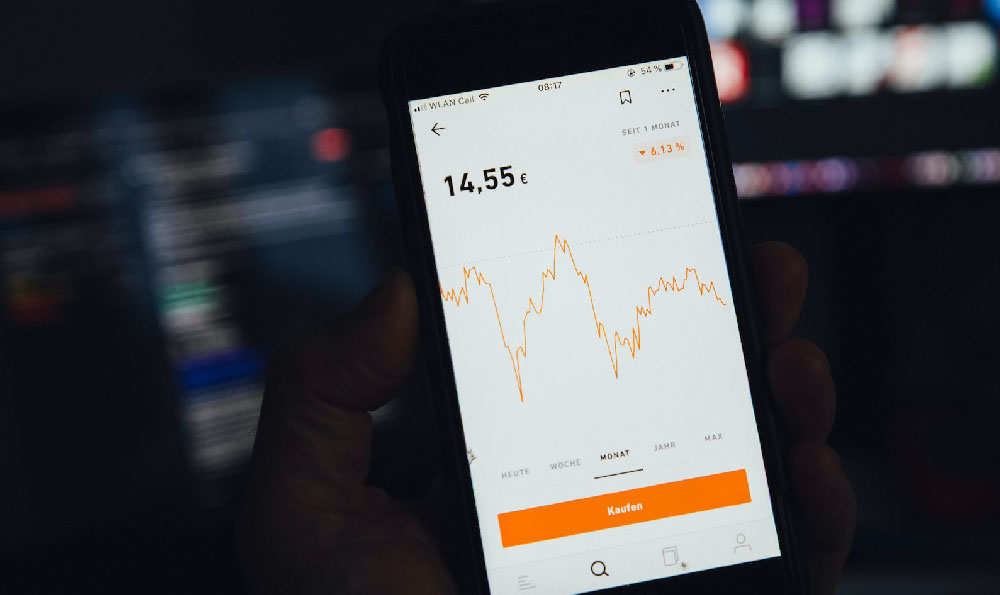
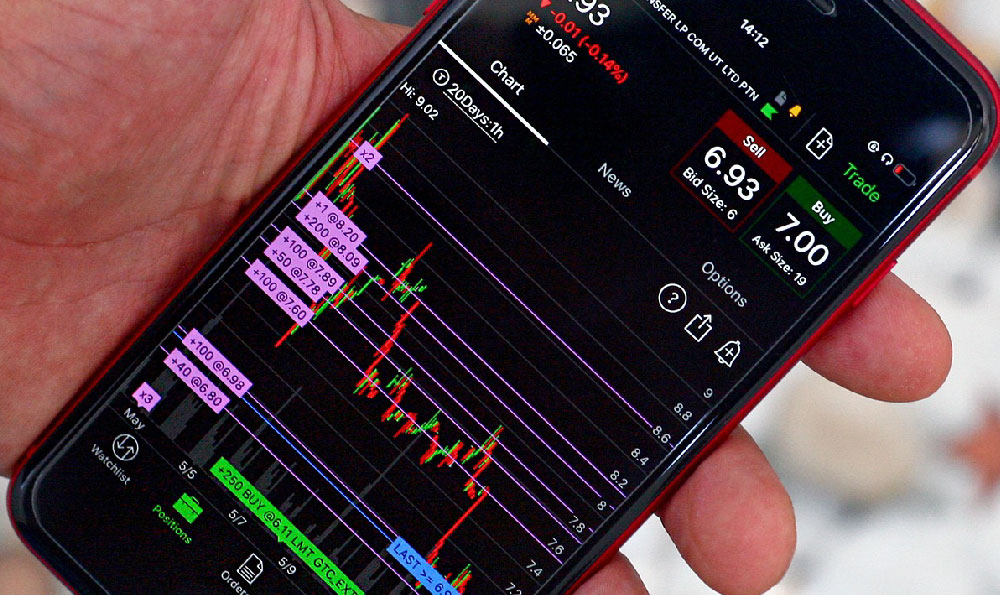
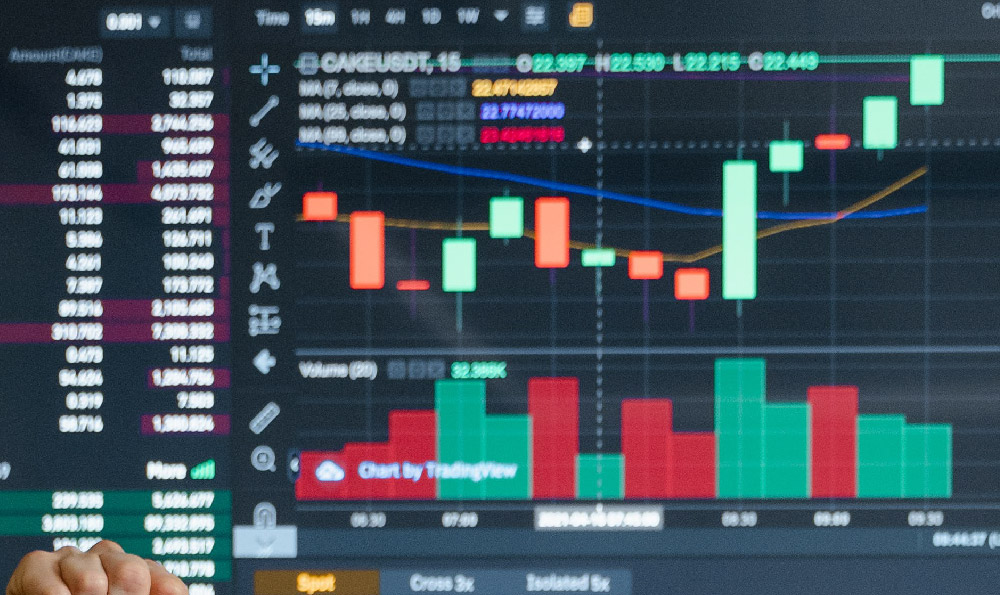
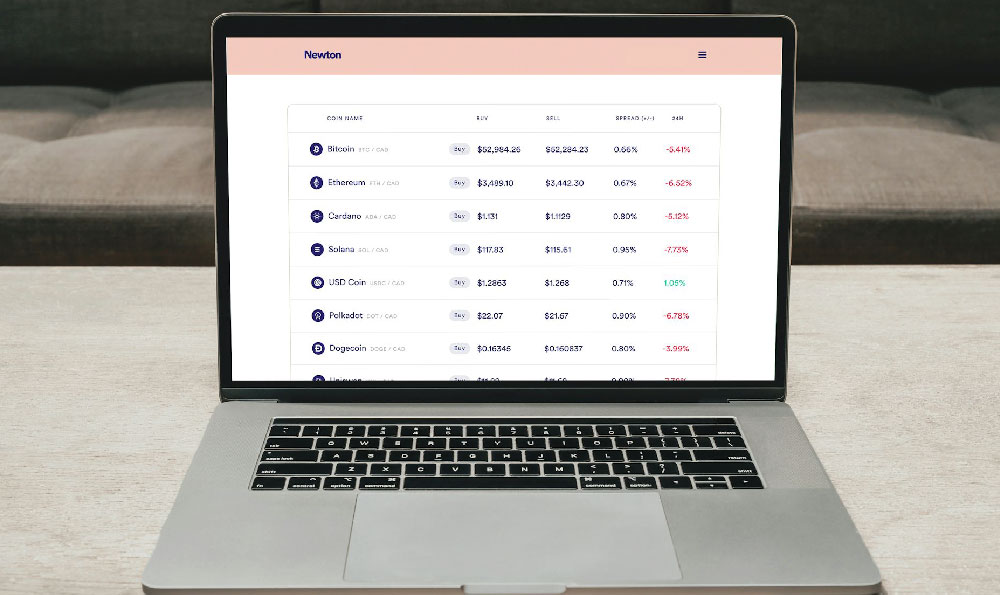
Investing in stocks is a cornerstone of wealth building for many, offering the potential for significant returns. However, approaching the stock market without a sound understanding of its intricacies can be a recipe for disaster. It's crucial to delve into the mechanics of stock investment and evaluate whether it aligns with your financial goals and risk tolerance.
Before diving into specific strategies, let's address the fundamental question: Is stock investing profitable? The short answer is yes, historically, the stock market has demonstrated the capacity to generate substantial profits. Over the long term, equities have consistently outperformed other asset classes like bonds or cash. However, this potential profitability comes with inherent volatility. The value of stocks can fluctuate dramatically due to various factors, including economic conditions, company performance, and investor sentiment. Therefore, profit isn't guaranteed, and losses are a very real possibility.
The first step in navigating the stock market is to define your investment goals. Are you saving for retirement decades down the line, or are you looking for shorter-term gains? Your time horizon directly influences the type of stocks you should consider and the level of risk you should assume. For long-term goals, you might be comfortable investing in growth stocks, which are companies with high potential for future earnings but also carry higher volatility. For shorter-term goals, you might prefer value stocks, which are companies that are undervalued by the market and offer a more stable investment.

Once you've defined your goals, you need to understand the different avenues for investing in stocks. You can purchase individual stocks directly, which allows you to have complete control over your portfolio. However, this requires significant research and understanding of individual companies and their financial health. Alternatively, you can invest in mutual funds or exchange-traded funds (ETFs). These are diversified portfolios of stocks managed by professional fund managers. Mutual funds are actively managed, meaning the fund manager actively buys and sells stocks to try to outperform the market. ETFs, on the other hand, are typically passively managed, tracking a specific market index like the S&P 500. ETFs generally have lower fees than mutual funds, making them a cost-effective option for beginners.
Choosing individual stocks requires a thorough analysis of the company. This involves examining its financial statements, including its income statement, balance sheet, and cash flow statement. You need to understand the company's revenue, expenses, profitability, debt levels, and cash flow generation. Furthermore, you should analyze the company's industry, its competitive landscape, and its management team. Are they innovative? Do they have a strong track record? What are their growth prospects? These are all crucial questions to consider. Technical analysis, using charts and patterns to predict future price movements, can be a complementary tool but should not be relied upon solely. A solid foundation in fundamental analysis is essential.
Regardless of your chosen investment strategy, diversification is paramount. Don't put all your eggs in one basket. Spreading your investments across different sectors, industries, and geographic regions can help mitigate risk. If one sector experiences a downturn, your overall portfolio will be less affected. Diversification doesn't eliminate risk entirely, but it can significantly reduce the impact of negative events on your investment returns.
Another crucial aspect of stock investing is understanding risk management. Before investing any money, determine your risk tolerance. How much are you willing to lose? Your risk tolerance should be based on your financial situation, your time horizon, and your personal preferences. Once you know your risk tolerance, you can develop a risk management strategy. This might involve setting stop-loss orders, which automatically sell your stocks if they fall below a certain price. It could also involve rebalancing your portfolio regularly to maintain your desired asset allocation.
Beyond specific investment strategies, it's critical to be aware of common investment pitfalls. Emotional decision-making is one of the biggest dangers. Fear and greed can lead to impulsive buying and selling, which can often result in losses. Avoid chasing hot stocks or panicking during market downturns. Stick to your investment plan and make rational decisions based on your analysis. Another pitfall is ignoring fees. Trading fees, management fees, and other expenses can eat into your returns over time. Choose low-cost investment options whenever possible. Finally, be wary of get-rich-quick schemes and unrealistic promises. If something sounds too good to be true, it probably is. Always do your own research and consult with a qualified financial advisor before making any investment decisions.
Continuous learning is essential for successful stock investing. The market is constantly evolving, and you need to stay informed about new trends, regulations, and investment strategies. Read books, articles, and financial reports. Attend seminars and webinars. Follow reputable financial news sources. The more you know, the better equipped you'll be to make informed investment decisions.
In conclusion, investing in stocks can be a profitable way to grow your wealth, but it requires careful planning, diligent research, and a disciplined approach. By defining your goals, understanding the different investment options, diversifying your portfolio, managing your risk, and continuously learning, you can increase your chances of success in the stock market. Remember that investing involves risk, and there are no guarantees. However, with the right knowledge and strategy, you can navigate the market effectively and achieve your financial goals. A final word of caution: never invest more than you can afford to lose.