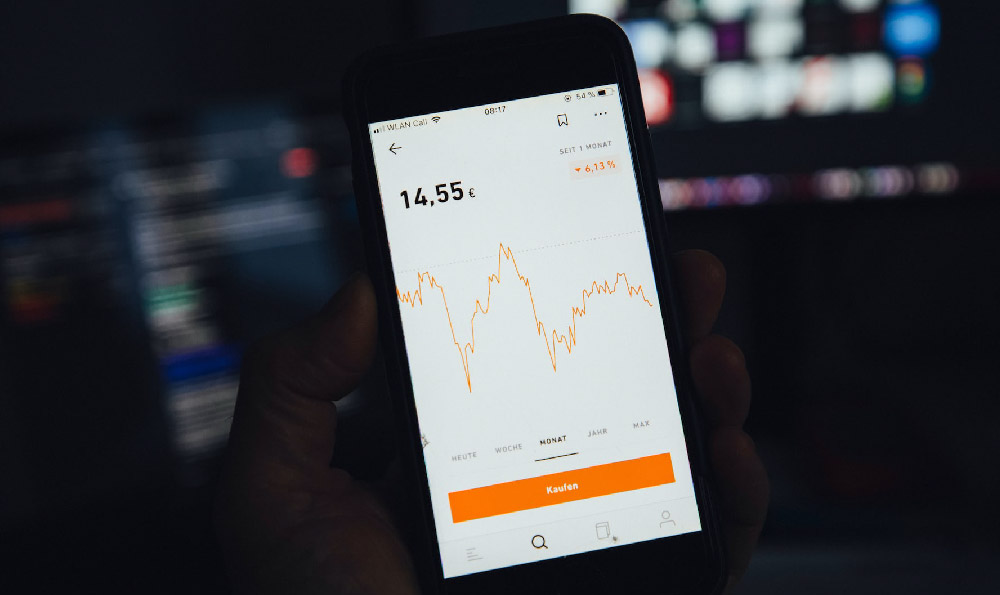
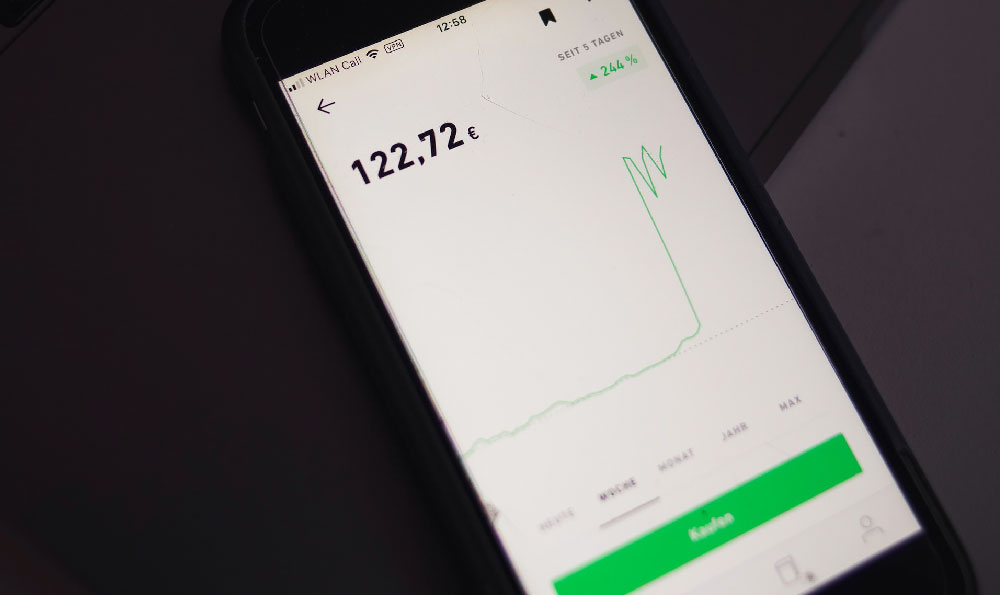
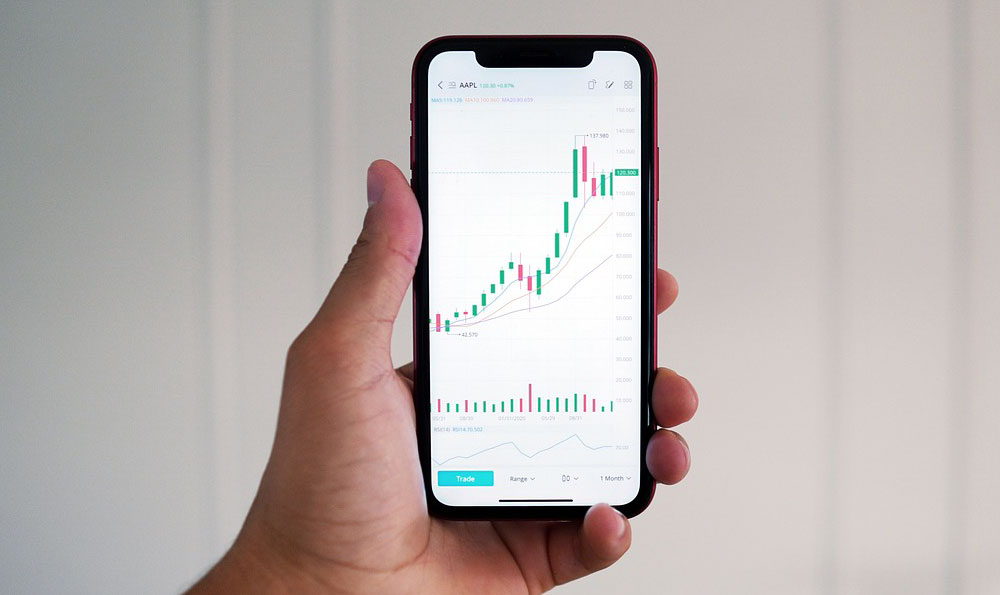
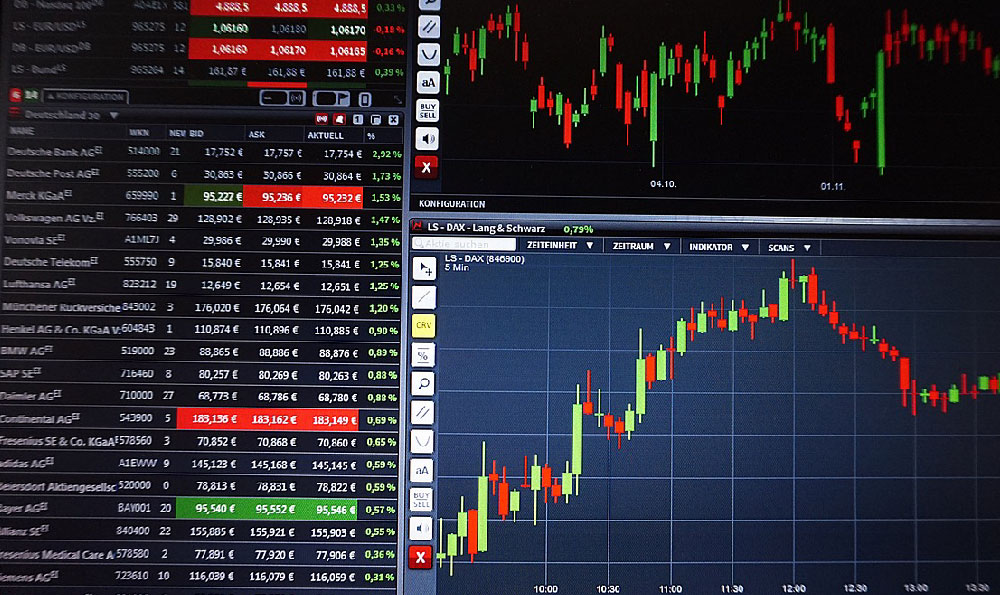
Embarking on the journey of stock market investing can feel like stepping into a complex maze, filled with unfamiliar jargon, fluctuating numbers, and the ever-present risk of financial loss. However, with the right knowledge, a solid strategy, and a disciplined approach, navigating this maze can lead to significant wealth creation over time. The key lies in understanding the various investment strategies available and knowing how to apply them effectively based on your individual circumstances and financial goals.
Before delving into specific strategies, it's crucial to lay a foundation of basic understanding. The stock market, at its core, is a platform where investors buy and sell shares of ownership in publicly traded companies. These shares, also known as stocks, represent a claim on a portion of the company's assets and future earnings. The value of these shares fluctuates based on various factors, including company performance, industry trends, economic conditions, and investor sentiment. Successfully investing in stocks requires careful analysis of these factors and the ability to make informed decisions.
One of the most fundamental and widely adopted investment strategies is value investing. This approach, popularized by legendary investor Warren Buffett, focuses on identifying companies that are currently undervalued by the market. Value investors believe that the market sometimes misprices stocks due to short-term negative news, temporary market downturns, or simply a lack of investor attention. They seek out companies with strong fundamentals, such as consistent profitability, healthy balance sheets, and competent management, that are trading at a price below their intrinsic value. Calculating intrinsic value is a crucial step, and it often involves analyzing financial statements, comparing the company to its peers, and estimating its future cash flows. Patience is paramount for value investors, as it may take time for the market to recognize the true worth of these undervalued companies.

In contrast to value investing, growth investing focuses on identifying companies with high growth potential, even if they are currently trading at relatively high valuations. Growth investors are willing to pay a premium for companies that are expected to experience rapid revenue and earnings growth in the future. These companies often operate in innovative industries, possess disruptive technologies, or have a strong competitive advantage. While growth investing can potentially deliver significant returns, it also carries a higher level of risk. Growth companies are often more sensitive to changes in market conditions and investor sentiment, and their valuations can be volatile. Thorough research is essential to assess the sustainability of a company's growth prospects and the reasonableness of its valuation.
Beyond these fundamental strategies, there are more specialized approaches such as dividend investing. Dividend investing focuses on companies that consistently pay out a portion of their profits to shareholders in the form of dividends. This strategy is particularly attractive to investors seeking a steady stream of income, such as retirees or those approaching retirement. Dividend-paying stocks tend to be more stable and less volatile than growth stocks, providing a cushion during market downturns. However, it's important to remember that dividend payments are not guaranteed and can be reduced or eliminated by companies at any time. Therefore, it's crucial to select companies with a history of consistent dividend payments and a strong financial position to support future payouts.
Another approach, momentum investing, capitalizes on the tendency of stocks that have been performing well to continue performing well in the short term. Momentum investors look for stocks that are exhibiting strong price appreciation and buy them in anticipation of further gains. This strategy is based on the idea that market trends can persist for a period of time, allowing investors to profit from the upward momentum. However, momentum investing is inherently riskier than value or dividend investing, as it relies on short-term price movements and can be susceptible to sudden reversals. It requires constant monitoring and a disciplined approach to risk management.
For those just starting out, understanding where to begin is paramount. The first step is to define your investment goals and risk tolerance. What are you hoping to achieve through investing? Are you saving for retirement, a down payment on a house, or simply building wealth? How much risk are you willing to take to achieve your goals? Answering these questions will help you determine the appropriate investment strategy and the amount of money you should allocate to stocks.
Next, open a brokerage account. There are many online brokers available, offering a range of services and fees. Research different brokers and choose one that meets your needs. Consider factors such as trading commissions, account minimums, research tools, and customer service. Many brokers also offer educational resources to help beginners learn about investing.
A highly recommended approach for beginners is to start with index funds or exchange-traded funds (ETFs). These funds offer instant diversification by investing in a basket of stocks that track a specific market index, such as the S&P 500. Index funds and ETFs are generally low-cost and provide broad exposure to the stock market, reducing the risk associated with investing in individual stocks. As you gain more experience and knowledge, you can gradually start to invest in individual stocks.
Before making any investment decisions, conduct thorough research. Read company financial statements, analyze industry trends, and stay informed about market news. Utilize the research tools provided by your broker or subscribe to reputable financial publications. Remember, knowledge is your greatest asset in the stock market.
Finally, develop a long-term investment plan and stick to it. The stock market can be volatile in the short term, but historically it has delivered strong returns over the long term. Avoid making emotional decisions based on short-term market fluctuations. Stay focused on your long-term goals and rebalance your portfolio periodically to maintain your desired asset allocation. Investing in stocks is a marathon, not a sprint. With patience, discipline, and a sound investment strategy, you can achieve your financial goals and build a secure future. Remember that past performance is not indicative of future results, and all investments carry risk. Consider consulting with a qualified financial advisor before making any investment decisions.